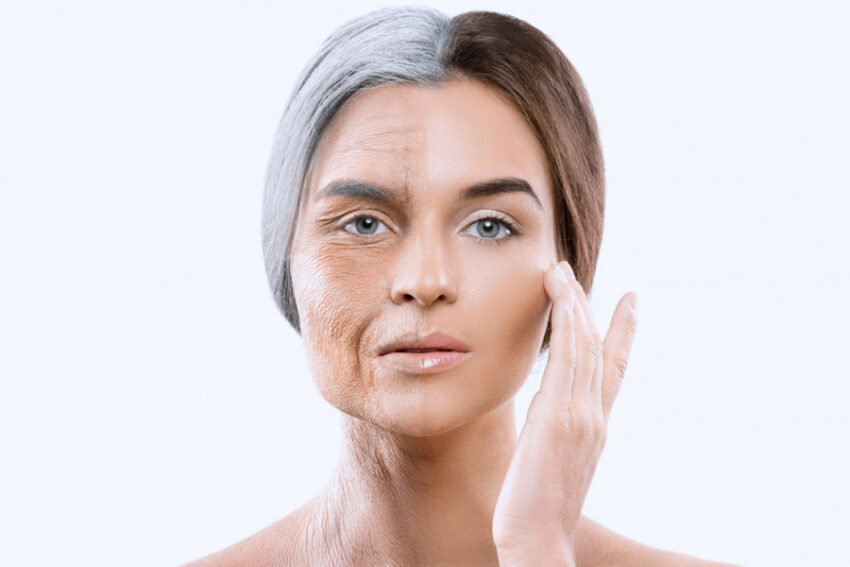
Glycation is a natural process that occurs in our body when excess sugar molecules react with proteins and fats, forming advanced glycation end-products (AGEs). This process is a significant contributor to skin aging, and one of the visible signs is the formation of wrinkles.
High glucose levels in our body can accelerate the glycation process and lead to the formation of more AGEs, which can cause more severe skin damage.
In addition to wrinkles, glycation can contribute to other visible signs of skin aging, such as fine lines, hyperpigmentation, and loss of skin elasticity. AGEs can also make the skin more susceptible to damage from environmental factors, such as UV radiation and pollution.
Apart from high glucose levels, other factors can accelerate the glycation process, including smoking, a diet high in processed and fried foods, and high alcohol consumption. These factors can increase oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, leading to more glycation and AGE formation.
Preventing glycation and its effects on the skin requires a multifaceted approach. In addition to controlling glucose levels and following a healthy diet, other lifestyle modifications can help slow down the glycation process. These include quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and avoiding exposure to environmental toxins.
Skincare products that contain ingredients that can prevent or reduce glycation can also be beneficial. Vitamin C, for example, is a potent antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals and protect collagen and elastin fibers from damage.
Niacinamide is another ingredient that has been shown to reduce AGE formation and improve skin elasticity. Carnosine is a dipeptide that can prevent cross-linking between proteins and reduce glycation.
To understand the impact of glycation on skin aging, let’s take the example of a person with uncontrolled diabetes.
Diabetes is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Over time, high glucose levels can lead to the formation of AGEs, which can damage collagen and elastin fibers in the skin. Collagen and elastin are essential proteins that maintain the skin’s elasticity and firmness.
When these proteins break down, the skin becomes saggy, thin, and wrinkled. A person with uncontrolled diabetes is likely to experience premature skin aging, and wrinkles may appear at a younger age.
Prevention/Management:
Prevention and management of glycation and skin aging require a holistic approach that involves lifestyle modifications and skincare routines.
1. Control glucose levels
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial to prevent glycation and skin aging. People with diabetes should follow their doctor’s recommendations and take their medication as prescribed.
2. Balanced diet
A diet that is low in processed foods and high in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help prevent glycation. Foods rich in antioxidants can also help neutralize free radicals that can damage the skin.
3. Skincare routine
Using skincare products that contain ingredients that can prevent or reduce glycation, such as vitamin C, niacinamide, and carnosine, can be beneficial. These ingredients can help protect collagen and elastin fibers and promote skin elasticity and firmness.
Conclusion
Glycation is a natural process that occurs in our body and contributes to skin aging, specifically the formation of wrinkles. High glucose levels can accelerate the glycation process and lead to the formation of more AGEs, which can cause severe skin damage.
Prevention and management of glycation and skin aging require a holistic approach that involves lifestyle modifications and skincare routines.
By controlling glucose levels, following a balanced diet, and using skincare products that contain ingredients that can prevent or reduce glycation, we can slow down the skin aging process and maintain youthful-looking skin.
Image by Freepik

Anvi has done Bachelor’s and Master’s in Nutrition and Dietetics. She’s planning to do a Ph.D. in Public Health Nutrition moving forward.





































Leave a Reply